| COLL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
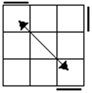
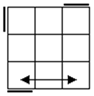
| Each OLL has the 14 PLL's underneath it. (S is
the 14th, solved) (AG are 3 cycles which can be treated as adjacent 2
cycles,TRFJ are adjacent 2 cycles ,EVYN are diagonal 2 cycles,UHZS are the
solved cases |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
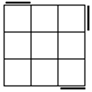
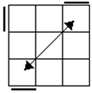
| The 2 diagonal swap cases are really the same case
if we ignore edges. So only one COLL will be needed, and by
extension, only one sub family of ZBll will be under it. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
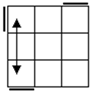
| All the three cycles and adjacent two cycles will
be handled together. There are 4 2-cycles, R corners, L corners, F corners, B
corners. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| The solved cases are all one case. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| This means that there are 6 possible COLL's for
each OLL, and most of them are the adjacent 2-swaps which can be solved with mirrors of the same
algorithm if the OLL is symmetric. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Other
sources |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| http://sarah.cubing.net/3x3x3/ocllcp#alg/coll-U4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| http://www.ai.univ-paris8.fr/~bh/cube/solutions_567.html |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| http://cubewhiz.com/coll.php |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| PDF
of compact version of this page |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
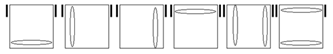
| Case 1 |
Case 2 |
Case 3 |
Case 4 |
Case 5 |
Recognition |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
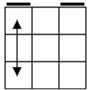
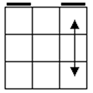
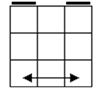
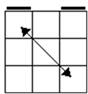
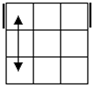
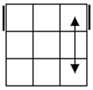
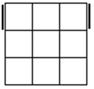
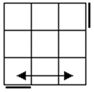
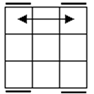
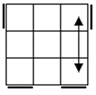
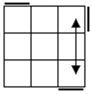
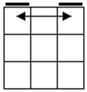
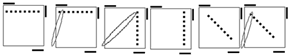
Check
for bars. Bars on both means case 1. Bars only on
headlights means the old alg, the other case is the soved PLL which can be solved with 2 sunes. If
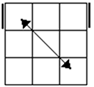
there are no bars then we have the diagonal case. If there are 2
diagonals, we have case 3. Otherwise, the diagonal's direction tells you
which slice to 180 first. Namely, the slice that has a properly oriented
corner of the diagonal is the one you turn first. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| (y) (R' U' R) (F R2 D') (R U R') (D R2 U' F') |
(R2 D') (R U2) (R' D) (R U2 R) |
(L2 D') (L' U2) (L D') (L' U2 L') |
(y2) R' F2 R U2 R U2 R' F2 R U2 R' |
(R' U2) (R F' R' F) U2 (F' R F) |
(R' U') (R U') (R' U2) (R2' U R' U) (R U2' R') |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
[U2] (L2' D') (L U2) (L' D) (L U2 L) |
[U2] (R2' D) (R' U2) (R D') (R' U2 R') |
R' U2 x R U' R' U B2 U' R U x' |
|
(y') R U R' U' R U' R' U2 R U' R' U2 R U R' |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
(y) (R U2 R' U' R U' R') (L' U2 L U L' U L) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
B U L' B D' B D B2 L2 U' L' B' |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
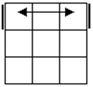
| Case 1 |
Case 2 |
Case 3 |
Case 4 |
Case 5 |
Recognition |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
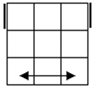
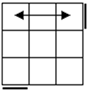
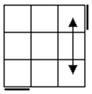
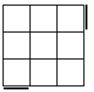
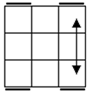
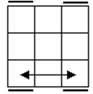
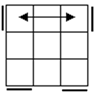
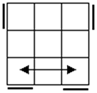
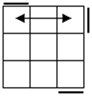
All
these cases have bars. Parallel bars are case 4 if they run up-down,
left-right bars are the solved case. After that, a single bar represents the
rest of the cases. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| (R' U) (R U2') L' (R' U R U') L |
(y') (rUR'U') (r'F'RF') |
(y) (l'U'LU) (lF'L'F) |
[U2] F (R U R' U') (R U' R' U') (R U R') F' |
(R' U R2' D) (Rw' U2) (Rw D') (R2 U' R) |
(y) (L'U'L U'L'U2L) (R'URURU2R') |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| (y2) L' U L U2 R' L' U L U' R |
|
y F(RUR'U') (RUR'U')F' (RUR'U') (R'FRF') |
(y) R U2 R' F2 R U2 R' U2 R' F2 R |
|
(R U2) (R' U' R U') (R2' U2) (R U R' U R) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
R U' R' U2 R U R' U2 R U R' U R U' R' |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
B L U L2 B2 D' B' D B' L U' B' |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
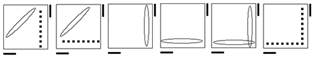
| Case 1 |
Case 2 |
Case 3 |
Case 4 |
Recognition |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
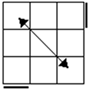
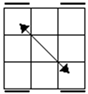
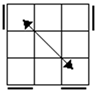
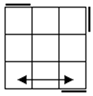
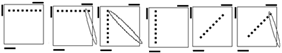
Case
one has a diagonal matching pair. The opposite color of the matching pair is
perpendicular to the first axis of turning. Case 2 is the standard OLL case
most people use. The first fat slice turn will break the axis of the matching
pair. Case 3 looks like case 2 but has two matching pairs. Case 4 has no
matching pairs. If you get it from the y2 angle, FUR matches ULF and RUF
matches URB. Since it is 2-gen and symmetric, it can be done from any angle
as an L or R sune. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| y' (R' U2 R' D') (R U2) (R' D R2') |
(R U2 R D) (R' U2) (R D' R2') |
Fl'U'LURU'r' |
R'FR y R'F'L'FR |
(RU2rB'r')(U2R) (rB'r') (U) |
(y2) (RU2R'U') (RUR'U') (RUR'U') (R U' R') |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| (y) (L' U2 L' D') (L U2)
(L' D L2') |
|
(y) LF'L' y' LFRF'L' |
y' (FR'F'R) (URU'R') F(URU'R') (URU'R')F' |
(y) (L' U2) (R U') (R' U2) L (R U' R') |
(LU2L'U') (LUL'U') (LUL'U') (LU'L') |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
y2 (F'LFL') (U'L'UL)F'(U'L'UL)(U'L'UL)F |
|
|
y R U' L' U R' U' R U R' U' L U R U' R |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
y B R' D2 R B' U2 B R' D2 R B' U2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
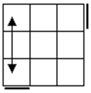
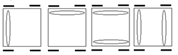
| Case 1 |
Case 2 |
Case 3 |
Case 4 |
Recognition |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| [U] F' (L' U L U') (L' U2 L U) (L' U' L U) F |
[U'] F (R U' R' U) (R U2 R' U') (R U R' U') F' |
[U'] (R U R' U) (R U) (Rw' F) (R' F' Rw) |
y' LUL'ULUR'UL'U'R |
F (R U R' U') (R U R' U') (R U R' U') F' |
(RU2R'U') (RU'R'U) (RU'R') |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
(y') R U R' U R U L' U R' U' L |
|
|
y (RUR'U) (RUR'U') (RU2R') |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
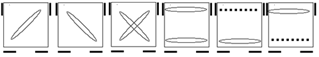
| Case 1 |
Case 2 |
Case 3 |
Case 4 |
Case 5 |
Recognition |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| [U] (R' F2) (R U2) (R U2) (R' F2) (U' R U' R') |
(R' U2) (R U R' U) (R2 U') (Rw' F) (R' F' Rw) |
y2 F (URU'R')(URU2R') (U'RUR') F' |
y R'ULU'R U'L'U'LU'L' |
y R U D' R U R' D R2 U' R' U' R2 U2 R |
y f(RUR'U') S' (RUR'U')F' |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
R U R' U F2 R U2 R' U2 R' F2 R |
y2 F R2 U' R2' U R2 U y L' R U2 R' |
(y') L' U R U' L U' R' U' R U' R' |
[U] F (R2 U') (R U') (R U') (R' U2) (R' U R2) F' |
y F(RUR'U') (RUR'U')F'(RUR'U') M'URU'r' |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
y R U2 R2 U' R2 U' R2 U2 R |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Case
1-niklas |
Case 2 |
Case 3 |
Case 4 |
Case 5 |
Case 6-sune |
Recognition |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| RU'L'UR'U'L |
RL'U R'U'LU2RU2R' |
z U' R2 U R2 D R' U' R UD' z' |
y' RUR'URU'RDR'U'RD'R2 |
(U2) R U R' U Rw' F R F' Rw U2 R' |
RUR'URU2R' |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
R2' F R U R U' R' F' R U' R' U R |
U2 L U L' U' L F' L' U' L U L F L2 |
U2 R U' R U' R' U R' U' y R U' R' |
|
(RU'L'UR'U'LU) (R'FR'B2RF'R'B2R2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
M F R' F' Rw U2' R U2' R' |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Case 1 |
Case 2 |
Case 3 |
Case 4 |
Case 5 |
Case 6 |
Recognition |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| L' U R U'
L U R' |
L' R U' L U R' U2 L' U2 L |
U2 (R'U'RUR') F (RUR'U'R') F' R2 |
y L' U' L U' L' U
L' D' L U L' D L2 |
U2 R U2 Rw' F R' F' Rw U' R U' R' |
L' U' L U' L' U2
L |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
L2 F' L' U' L' U L F L' U L U' L' |
z' U L2 U' L2 D' L U L' U' D z |
U2 L' U L' U L U' L U y' L' U L |
|
L' U R U' L U R' U' L F' L B2 L' F L B2 L2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
M F' L F L' U2 L' U2 L |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|